Blog
News, guides, and insights about self-hosted GitHub Actions runners.
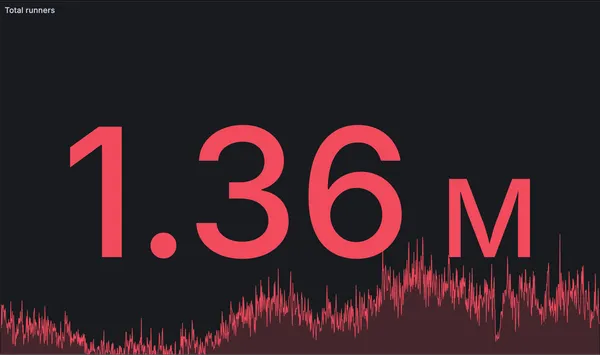
New record: 1.36 million GitHub Actions jobs in a single day
RunsOn hits a new record with 1.36 million GitHub Actions jobs processed in a single day, up from 990k just six weeks ago.

BuildJet Is Shutting Down. What Should GitHub Actions Teams Do Next?
BuildJet announced it is discontinuing service. Here is what this means for the GitHub Actions market and why RunsOn is a strong BuildJet alternative for performance, flexibility, and cost.

From freelancer to running ~1.5% of all GitHub Actions jobs: Building RunsOn as a solo founder
How frustrations with CI/CD bottlenecks turned into RunsOn and scaled to 1.18M jobs per day.
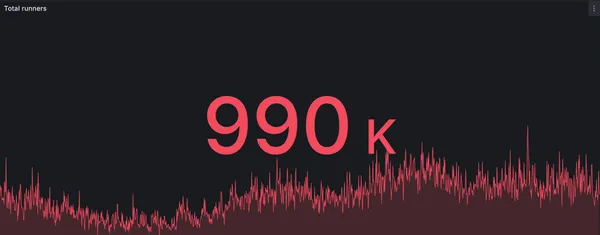
New record: RunsOn processes 990k jobs in a single day
RunsOn hits a new milestone with nearly 1 million GitHub Actions jobs processed in a single day

GitHub to charge $0.002/min for self-hosted runners starting March 2026
GitHub announced upcoming billing changes for self-hosted runners. We've updated our pricing calculator and tables so you can see exactly how this affects your CI costs.

Cloud-init tips and tricks for EC2 instances
Useful cloud-init commands to troubleshoot and inspect EC2 instances.
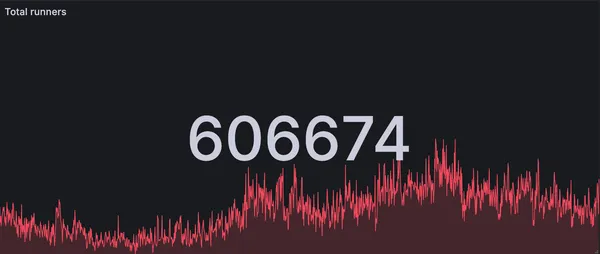
RunsOn is now handling more than 600k jobs per day
How we handle 600k+ jobs per day with RunsOn, the best solution for running GitHub Actions in your own infrastructure

Why smart developers choose ephemeral runners (and you should too)
Long-lived CI runners are technical debt disguised as optimization. Here's why ephemeral beats persistent every time.
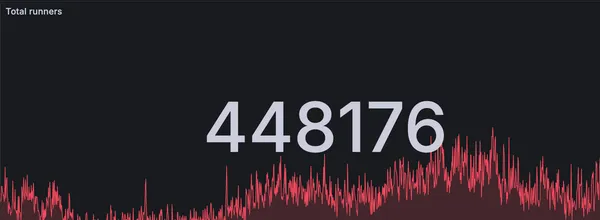
RunsOn is now handling more than 400k jobs per day
How we handle 400k+ jobs per day with RunsOn, the best solution for running GitHub Actions in your own infrastructure

The true cost of self-hosted GitHub Actions - Separating fact from fiction
Analysis of self-hosted GitHub Actions runners' costs and challenges, and how RunsOn solves these problems with minimal overhead and maximum savings.
🚀 v2.8.2 is out, with EFS, Ephemeral Registry support, and YOLO mode (tmpfs)!
Speed up docker builds with the ephemeral registry, share files across workflow jobs with EFS, and speed up your builds with tmpfs!
StepSecurity Partnership
RunsOn partners with StepSecurity to protect CI/CD runners from supply chain attacks. Learn about the integration that provides network monitoring, file integrity checks, and security insights for your GitHub Actions workflows.
v2.6.5 - Optimized GPU images, VpcEndpoint stack parameter, tags for custom runners
v2.6.4 and v2.6.5 have been released in the last weeks, with the following changes.
RunsOn is now handling 200k jobs per day
How we handle 200k jobs per day with RunsOn, the best solution for running GitHub Actions in your own infrastructure

Faire des économies avec ses propres runners
More about RunsOn (in French) in this podcast.

GitHub Actions are slow and expensive, what are the alternatives?
GitHub Actions are slow and expensive, what are the alternatives?

How to verify that VPC traffic to S3 is going through your S3 gateway?
Not properly checking your route tables could lead to high bills and slower throughput.

GitHub Actions runner images (AMI) for AWS EC2
Fast, optimized AWS AMIs for GitHub Actions runners. Updated every 2 weeks.

Use GitHub App manifests to symplify your GitHub App registration flow
Did you know you can automatically register a GitHub App with a GitHub App manifest? Learn how to use simple HTML forms and JavaScript to submit your app details to GitHub.

How to setup docker with NVIDIA GPU support on Ubuntu 22
Learn how to enable GPU support in Docker containers with CUDA drivers and nvidia-container-toolkit. Follow a step-by-step guide to install the necessary components and configure the runtime. Run the container with GPU enabled and check the GPU information with nvidia-smi.

Automatically cleanup outdated AMIs in all AWS regions
Learn how to automatically cleanup Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) that are older than a specific threshold, while keeping the 2 most recent AMIs in each region. This script helps remove outdated images and reduce storage costs for your AMIs.

How to setup GitHub hosted runner with a simple cloud-init script
Learn how to launch GitHub hosted runners non-interactively with a Bash script that can also be used as a cloud-init script. This blog post provides step-by-step instructions for installing Docker, additional packages, and creating a dedicated user.