Troubleshooting
Troubleshoot your RunsOn installation
Runners can fail to start for a variety of reasons. If an error is raised while attempting to start a workflow, RunsOn will alert you by email (assuming you have confirmed the SNS Topic notification when you setup the stack).
Quick checks
Section titled “Quick checks”- https://www.githubstatus.com ↗ - see if GitHub Action is having issues.
- you are using the latest version.
Contact support
Section titled “Contact support”Once you’ve made the checks above, please have a look below at various error cases, and send us an email if the issue persists: [email protected]. Include as many details as possible, such as:
- RunsOn version.
- AWS region.
- Any error messages you see in the GitHub UI, email notifications, or CloudWatch logs.
- CloudWatch logs for the AppRunner service (you can filter on the
run_idorjob_id), and instance logs if you have them. - Details about the workflows in error, especially the
runs-onlabels, number of jobs in the workflow, and any use of matrix jobs.
How to find run_id and job_id
Section titled “How to find run_id and job_id”The run_id and job_id are not easily available from the GitHub UI. The easiest way is to go to a job log outputs in the GitHub UI, and extract the values from the URL.
For instance you may have a URL that looks like this:
https://github.com/YOUR_ORG/YOUR_REPO/actions/runs/12054210358/job/33611707460In which case the run_id is 12054210358 and the job_id is 33611707460.
All jobs are queued indefinitely or long queuing time for some workflows
Section titled “All jobs are queued indefinitely or long queuing time for some workflows”RunsOn runners consistently start in ~30s for x64 and arm64. If you are seeing abnormal queuing times, let’s review the different possible root causes.
Webhooks not getting delivered
Section titled “Webhooks not getting delivered”To start a runner, the GitHub webhook needs to be delivered to the RunsOn AppRunner service. If you are seeing long queuing times, it is possible that the webhook is not getting delivered.
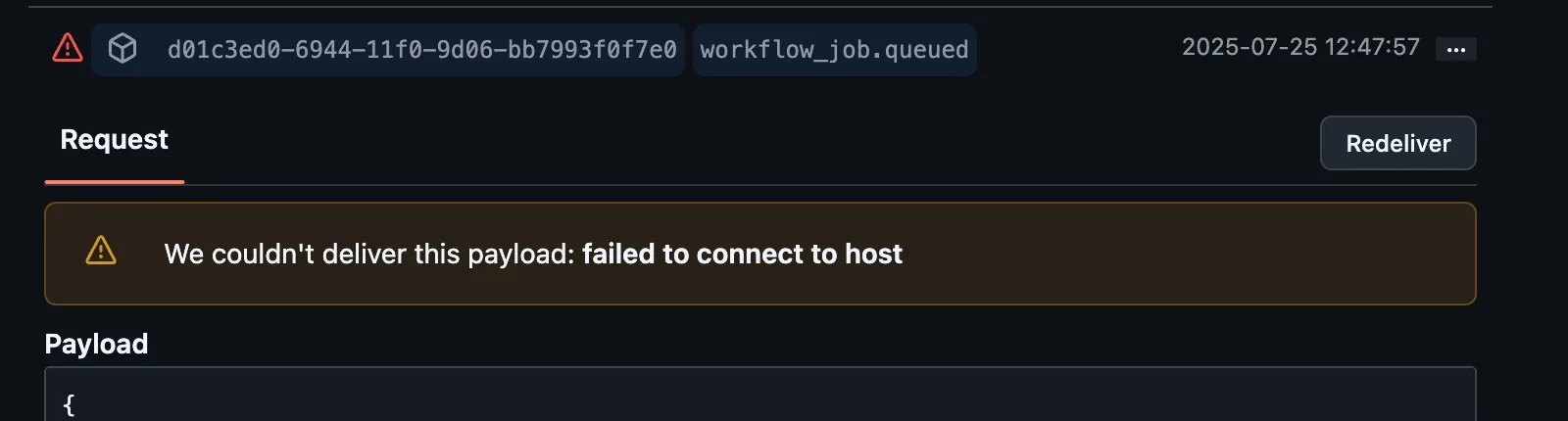
To check this, you can go to your RunsOn GitHub App settings > Advanced, and you should see the last deliveries with their status code.
If you see a non-200 status code, it is possible that the webhook is not getting delivered. You can manually trigger a delivery. If it persists and you think it might be a bug on the receiver side (RunsOn AppRunner service), please contact support.
Runner stealing
Section titled “Runner stealing”It may be the case that the runner started for your workflow job has been stolen by another workflow job.
For instance, if two workflow jobs A and B with the same runs-on labels are queued at the same time, the runner started for job A may actually start processing job B (since runner A labels matches those for job B), while job A has to wait for runner B to come up online.
To avoid this and help with debugging, it is best practice to ensure that each workflow job gets a more unique label. This can be achieved by assigning the current workflow run id as an additional label.
Make sure you are using the new single label syntax available since v2.5.4, to ensure as much determinism in label name as possible:
jobs: my-build-job: runs-on: "runs-on=${{ github.run_id }}/runner=2cpu-linux-x64" # even better, if you have multiple jobs in the same workflow file with the same `runs-on:` labels runs-on: "runs-on=${{ github.run_id }}-my-build-job/runner=2cpu-linux-x64"
my-release-job: runs-on: "runs-on=${{ github.run_id }}-my-release-job/runner=2cpu-linux-x64"If the problem persists:
- ensure that the repository is correctly enabled for your RunsOn GitHub App.
- ensure that webhooks are correctly delivered to your AppRunner service: go to your RunsOn GitHub App settings > Advanced, and you should see the last deliveries with their status code.
If you need more help, please contact support (see above for links).
Runner stealing and matrix jobs
Section titled “Runner stealing and matrix jobs”If you are using matrix jobs, note that the github.run_id is not unique for each matrix job. It is only unique for each workflow run, and unfortunately GitHub still doesn’t expose the JOB_ID variable for a job. So if you want to ensure a deterministic job <-> runner assignment, you can append the strategy job index ↗ in addition to the workflow run id. You can also add the run attempt number ↗ for good measure:
jobs: my-build-job: strategy: matrix: node: [16, 18, 20] runs-on: "runs-on=${{ github.run_id }}-my-build-job-${{ strategy.job-index }}/runner=2cpu-linux-x64" # or even more complete, although... long runs-on: "runs-on=${{ github.run_id }}-my-build-job-${{ github.run_attempt }}-${{ strategy.job-index }}/runner=2cpu-linux-x64"View the application logs
Section titled “View the application logs”Application logs for the RunsOn AppRunner service are available in CloudWatch, and the log group looks like this: /aws/apprunner/RunsOnService-2LsVa1bzgQUG/4bd58e13a7234899a9685f7b7e62b20c/application.
There are multiple ways to access the logs:
Using the RunsOn CLI
Section titled “Using the RunsOn CLI”Since v2.6.3, RunsOn provides a CLI to easily access all the logs related to a GitHub job, just by pasting the GitHub job URL in the command line:
AWS_PROFILE=your-aws-profile roc logs https://github.com/YOUR_ORG/YOUR_REPO/actions/runs/RUN_ID/job/JOB_IDYou will get the interleaved logs from the RunsOn AppRunner service, and the EC2 instance for its full lifecycle.
Note that for complete debugging, full logs of the AppServer may be required (see next section).
Using awslogs
Section titled “Using awslogs”It can be useful to access the logs of RunsOn to see more details about the issues. This can either be done from CloudWatch UI, or with awslogs command:
pip install awslogsNow replace the log group (/aws/apprunner/...) with yours, and you can do:
AWS_PROFILE=your-aws-profile awslogs get --aws-region eu-west-1 \ /aws/apprunner/RunsOnService-6Gwxsz1vjfMD/356d75069c2c4ec89b0e452c51778ce8/application \ -wGS -s 30m --timestampUsing the AWS Console
Section titled “Using the AWS Console”You can also find the logs from the AWS UI, and apply filtering based on e.g. the workflow run id:
Note: the log group created by the AppRunner application has no retention period set (not supported yet by CloudFormation). We recommend that you manually update this period to e.g. 30 days to avoid costs.
View the instance cloud-init logs
Section titled “View the instance cloud-init logs”The CloudWatch agent is automatically setup and started on all instances that use or derive from the official images.
Logs from the agent itself, and more importantly logs from the cloud-init boot process, are available in CloudWatch.
Using the RunsOn CLI
Section titled “Using the RunsOn CLI”You can use the RunsOn CLI to view all job logs:
roc logs https://github.com/owner/repo/actions/runs/123/job/456Using the AWS Console
Section titled “Using the AWS Console”These logs can be also be retrieved from the AWS UI: CloudWatch > Log groups > <STACK_NAME>-runs-on-EC2InstanceLogGroup-<RANDOM_ID>.
Within that log group you will find a log stream for each instance and accompanying log file (e.g. i-0006f3ff78fcd11f4/cloud-init-output). You can filter using the instance ID.
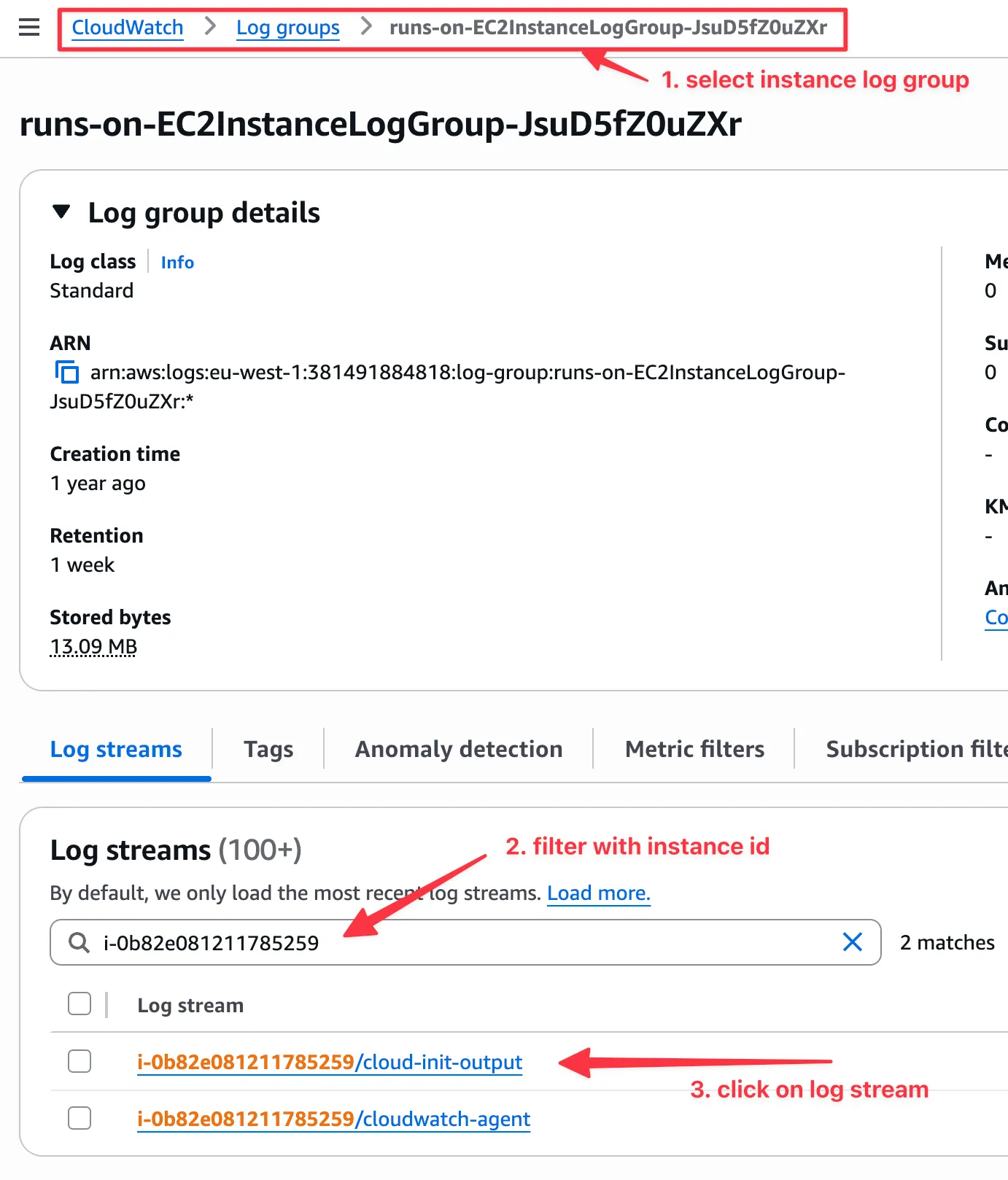
Instance logs are kept for 7 days.
View the instance console logs
Section titled “View the instance console logs”Using the RunsOn CLI
Section titled “Using the RunsOn CLI”You can use the RunsOn CLI to view the console logs:
roc logs https://github.com/owner/repo/actions/runs/123/job/456 --include=consoleUsing the AWS Console
Section titled “Using the AWS Console”You can also retrieve the console logs through the AWS Console. In EC2, select your instance and then Actions > Monitor and troubleshoot > Get system log:
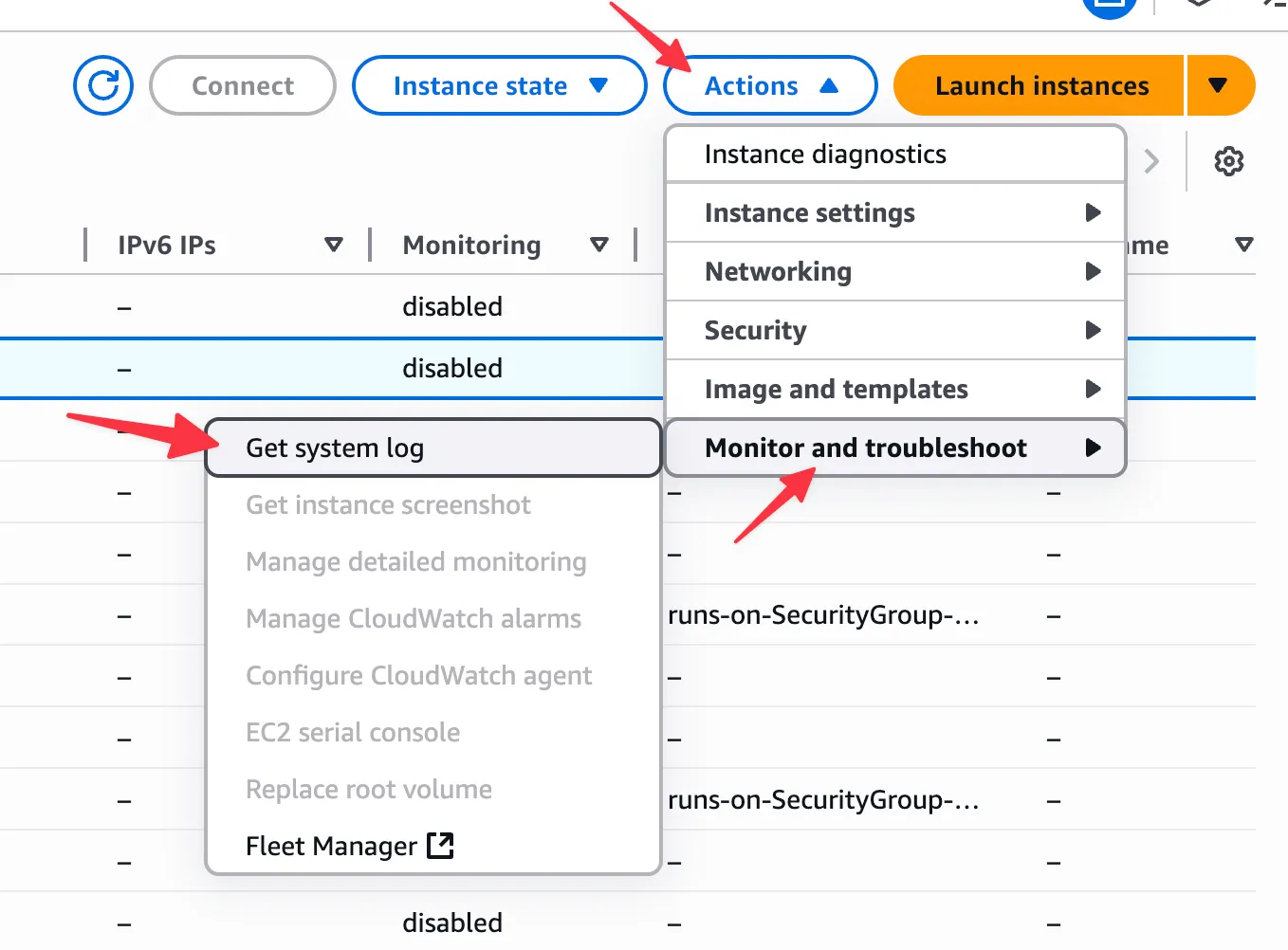
Note that system logs are sometimes only available a few minutes after the instance has been created.
View Cloudtrail events
Section titled “View Cloudtrail events”If you’re getting errors about request limit exceeded or quota issues, have a look at the Cloudtrail events, and especially for the RunInstances API event, to see if you are getting rate limited.
For instance in eu-west-1, the Cloudtrail events can be accessed at:
https://eu-west-1.console.aws.amazon.com/cloudtrailv2/home?region=eu-west-1#/events?ReadOnly=falseChecking if a spot instance has been preempted
Section titled “Checking if a spot instance has been preempted”In the CloudTrail events, you can check if a spot instance has been preempted by checking for events with the name BidEvictedEvent.
Failed to create instance
Section titled “Failed to create instance”This error can happen due to multiple reasons:
PendingVerification
Section titled “PendingVerification”⚠️ Failed to create instance with type c7a.4xlarge: PendingVerification: Your request for accessing resources in this region is being validated, and you will not be able to launch additional resources in this region until the validation is complete. We will notify you by email once your request has been validated. While normally resolved within minutes, please allow up to 4 hours for this process to complete. If the issue still persists, then open a support case. [https://support.console.aws.amazon.com/support/home?region=us-east-1#/case/create?issueType=customer-service&serviceCode=account-management&categoryCode=account-verification]This is usually resolved within a few minutes (automatically). So just retry the workflow a few minutes later and it should work. Otherwise open a support case.
RequestLimitExceeded
Section titled “RequestLimitExceeded”This usually happens if you are launching instances too quickly compared to the allowed rate limit for your account.
The rate limit mechanism is detailed in https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/APIReference/throttling.html ↗, but this should not longer happen since v1.6.2.
RunsOn now defaults to the lowest rate limit (2 RunInstances API call/s max).
If your account has a higher quota for those API calls, you can modify the queue size in the CloudFormation stack parameters to take advantage of it.
Unexpected costs
Section titled “Unexpected costs”AWS Config
Section titled “AWS Config”If you have AWS Config enabled in your AWS account, with the default settings it will record an event for every resource created in your account, including every EC2 instances created by RunsOn. Each EC2 instance will trigger at least 3 events that could quickly add up:
AWS EC2 FleetAWS EC2 Network InterfaceAWS EC2 Volume
To avoid this, you should modify your AWS Config settings to skip recording for those events, in the AWS account where RunsOn is deployed.
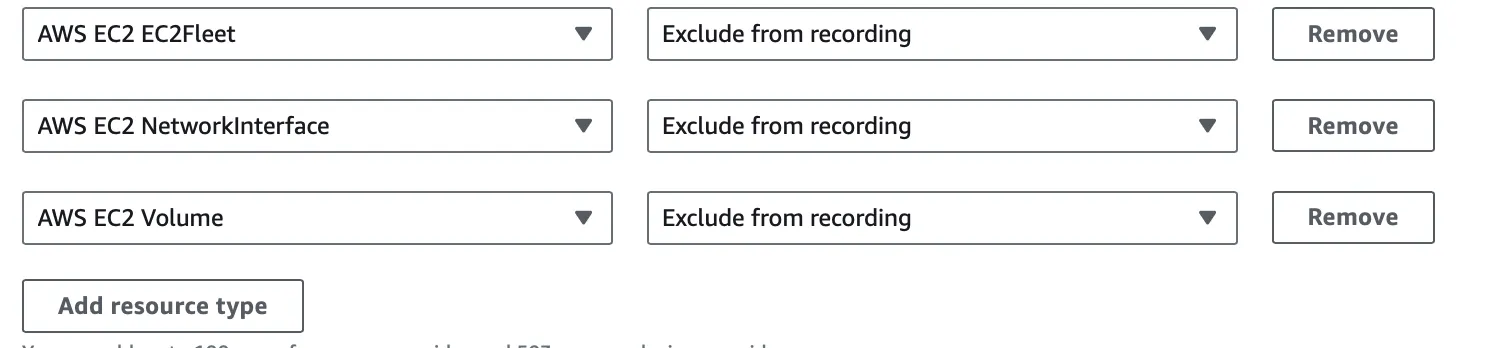
You can also skip recording AWS EC2 Instance events if you have really high usage.
Datadog
Section titled “Datadog”From one of our users ↗:
We ran into a big spike in registered Datadog Infra Hosts after switching to RunsOn because Datadog’s automatic AWS integration was picking up the new instances. And of course, since this is Datadog, more hosts means a lot more money. https://docs.datadoghq.com/account_management/billing/aws/#aws-resource-exclusion ↗ gives an easy approach to ignoring these hosts, I’m just doing
EC2: !provider:runs-on.comand that seems to be working.
Useful log filters
Section titled “Useful log filters”Below are some useful log filters that can be used to filter the logs in the CloudWatch console to look for specific events.
Spot interruption events
Section titled “Spot interruption events”EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning: appears when a Spot Instance is preempted.
Instance state changes
Section titled “Instance state changes”EC2 Instance State-change Notification: appears when an instance changes state.
{"level":"info","app_environment":"dev","app_stack_name":"runs-on","app_version":"v2.6.7-dev","event":{"version":"0","id":"40473256-175b-1dda-ce12-a89033da938a","detail-type":"EC2 Instance State-change Notification","source":"aws.ec2","account":"756351362063","time":"2025-02-14T15:56:59Z","region":"us-east-1","resources":["arn:aws:ec2:us-east-1:756351362063:instance/i-098becb5aa9dbf323"],"detail":{"instance-id":"i-098becb5aa9dbf323","state":"running"}},"time":"2025-02-14T16:56:59+01:00","message":"🗒️ Processing event"}Rate limiters
Section titled “Rate limiters”Current tokens: outputs the tokens remaining in each rate limit bucket.
{"level":"info","app_environment":"dev","app_stack_name":"runs-on","app_version":"v2.6.7-dev","time":"2025-02-14T16:39:17+01:00","message":"Current tokens remaining/used/limit for GitHub: 4395/605/5000, Self-Hosted Runners: 10000/0/10000. Next reset at 2025-02-14 16:55:25 (in 967.15 seconds, 4.54 tokens/s)"}{"level":"info","app_environment":"dev","app_stack_name":"runs-on","app_version":"v2.6.7-dev","time":"2025-02-14T16:39:17+01:00","message":"Current tokens remaining for limiters: githubLimiter=tokens:0.00,burst:4395 ec2ReadLimiter=tokens:100.00,burst:100 ec2RunLimiter=tokens:5.00,burst:5 ec2TerminateLimiter=tokens:5.00,burst:5 ec2MutatingLimiter=tokens:50.00,burst:50"}Notes:
- the Self-Hosted Runners rate limit is supposed go down, but GitHub currently doesn’t enforce (nor counts) it. So the GitHub API currently always returns 10000 remaining tokens.
- contrary to EC2, the GitHub rate limit is only refillable every hour. So once it goes down to zero, you will have to wait until the next hour to be able to run workflows again. RunsOn attempts to avoid this as much as possible and you should not hit the limit if you run up to 2000 jobs per hour (or 6000 jobs per hour on GitHub Enterprise plan).
